HEART CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
OR
BLOOD VASCULAR SYSTEM
The study of blood vascular system or circulatory system is called angiology
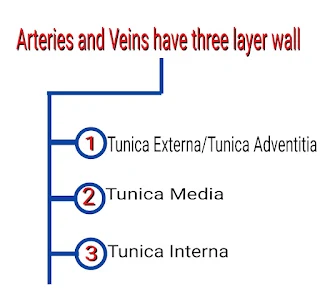
The vascular system is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph fluid through the body. It's also called the circulatory system. The arteries and veins carry blood all over the body. They send oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues.
BLOOD VESSELS
1 Arteries
2 Veins
3 Capillaries
Differentiate between arteries and vein
CAPILLARIES
They have only one layer i.e. simple squamous endothelium layer.
ANATOMY OF HEART
Heart is a coned shaped hollow structure equal to the size of puzzle fit.
It is a mesodermally derived organ, is situated in the thoracic cavity, in between the two lungs (mediastinum), slightly tilled to the left.
The heart weight between 200 to 425g.
The lower portion is apex and upper portion is base.
Wall of heart
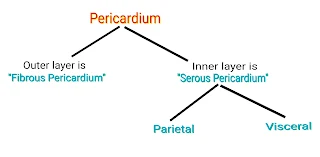
1. Pericardium
2. Myocardium
3. Endocardium
Pericardium-- It is a outermost layer of the heart.
Heart is protected by a double walled membranous bag like structure called pericardium.
Endocardium -- It consist of flatted epithelial cell and it is continuous with endothelium lining the blood vessels.
Mammals heart have a four chambers, two small upper chambers called atria and two large lower chambers called ventricles.
Inter-atrial septum wall separate the right and the left atria.
It is a thin muscular layer (wall).
Inter-ventricular septum wall separate the right and left ventricles.
It is a thick muscular wall.
Atrio-ventricualr septum separate the atrium and ventricles of the same side.
AORTIC ARCH
The aortic arch has 3 major branches.
The brachiocephalic trunk is the first branch of the aortic arch and supplies blood to the right arm and right head and neck.
The left common carotid artery is the second branch of the aortic arch, which supplies blood to the left side of the head and the neck.
The last branch of the aortic arch is the left subclavian artery that distribute blood to the left arm.
PULMONARY CIRCULATION
The deoxygenated blood pumped into the pulmonary artery is passed on to the lungs (from where the oxygenated blood is carried by the pulmonary veins into the left atrium) this pathway is called pulmonary circulation.
Pulmonary circulation occur only between the heart and lungs.
SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION
Circulation of blood throughout the body through the arteries, capillaries and veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to various tissue and return venous blood to the right atrium.
Systemic circulation occur between the heart and body.
CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF HEART
The cardiac conduction system is a group of specialized cardiac muscle cells in the walls of the heart.
That send signals to the heart muscle causing it to contract.
The main components of the cardiac conduction system are the SA Node, AV Node, bundle of his, bundle branches and Purkinje fibers.
FUNCTION OF SA NODE
(Sino-atrial node) or (Natural pacemaker of heart)
1. The SAN can generate the maximum number of action potential. i.e. 70-75 beats per minute (bpm).
2. It is responsible for initiating and maintaining the rhythmic contractile activity of the heart that's why it is called the natural pacemaker.
NOTE- Our heart normally beats 70-75 times in a minute.
(Average 72 beats per minute)
FUNCTION OF AV NODE
1. The purpose of this structure is to connect the electrical system of the atria and the Ventricles, providing electrical impedance from the atria and an intrinsic pacemaker in its absence.
2. The intrinsic rate of the AV node is 40-60 beats per minute (bpm).